What works: Health and care interventions to support people from disadvantaged backgrounds with musculoskeletal conditions
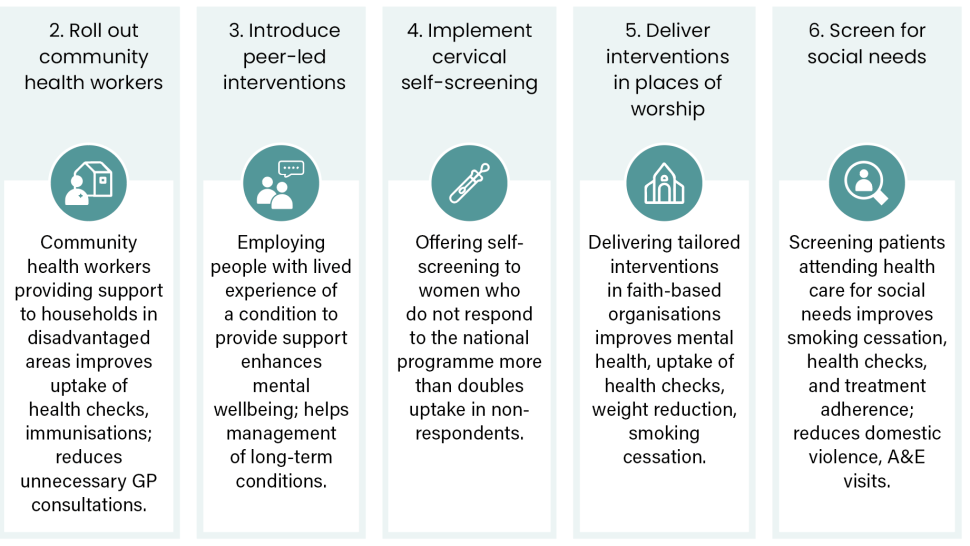
17.1 million people in England are estimated to be living with a musculoskeletal (MSK) condition. This evidence brief explores what health and care interventions work to improve outcomes for people from disadvantaged backgrounds, and what approaches are most effective in addressing the inequalities they face.